Moderna on Wednesday said clinical trial data showed its updated COVID-19 vaccine will likely be effective against the highly-mutated BA.2.86 subvariant of the coronavirus that has raised fears of a resurgence of infections.
The company said its shot generated an 8.7-fold increase in neutralizing antibodies in humans against BA.2.86, which is being tracked by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“We think this is news people will want to hear as they prepare to go out and get their fall boosters,” Moderna head of infectious diseases Jacqueline Miller said in an interview, adding that the data should also help reassure regulators.
The CDC has previously indicated that BA.2.86 may be more capable of causing infection in people who previously had COVID or were vaccinated with previous shots.
The Omicron offshoot carries more than 35 mutations in key portions of the virus compared with XBB.1.5, the dominant variant through most of 2023 and the target of the updated shots.
Moderna said it had shared the new finding on its vaccine with regulators and submitted it for peer review publication. The retooled shot has yet to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, but is expected to be available later this month or in early October.
The Massachusetts-based drugmaker and rival COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers Novavax and Pfizer with German partner BioNTech have created versions of their shots aimed at the XBB.1.5 subvariant.
Last month, Moderna and Pfizer each said their new vaccines appeared to be effective against another new subvariant of concern dubbed EG.5 in initial testing.
European regulators have since backed the Pfizer/BioNTech shot, with Britain's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency approving the vaccine on Tuesday, but have yet to make any announcements on Moderna’s updated vaccine.
BA.2.86 has now been detected in Switzerland and South Africa as well as Israel, Denmark, the US and Britain according to a WHO official.
While it is important to monitor the variant, several experts told Reuters it is unlikely to cause a wave of severe disease and death because of immune defences built up worldwide from mass vaccination and prior infection.
Moderna's shares rose marginally to $109.89 before the opening bell, erasing their premarket losses.
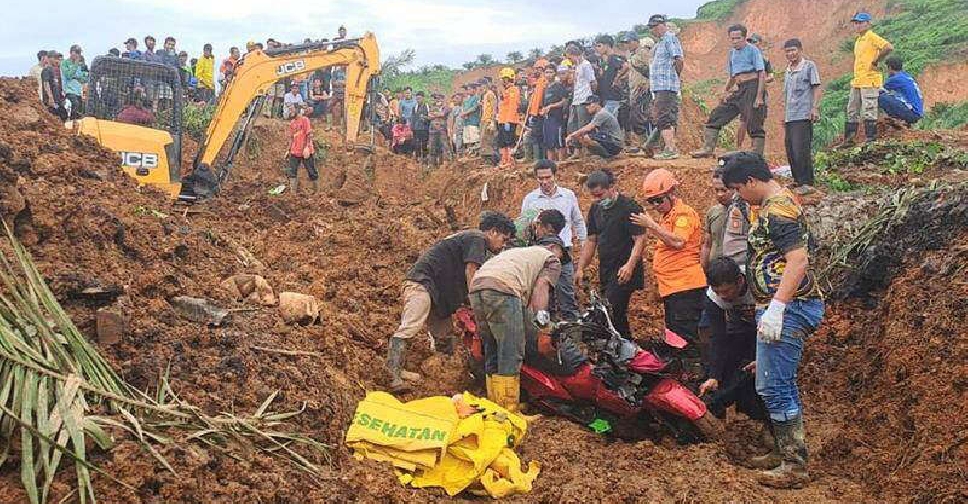


 Seven dead, 82 missing in Indonesian landslide
Seven dead, 82 missing in Indonesian landslide
 Bombing at Pakistan wedding kills 7, police say
Bombing at Pakistan wedding kills 7, police say
 Australian boy dies after shark attack in Sydney Harbour
Australian boy dies after shark attack in Sydney Harbour
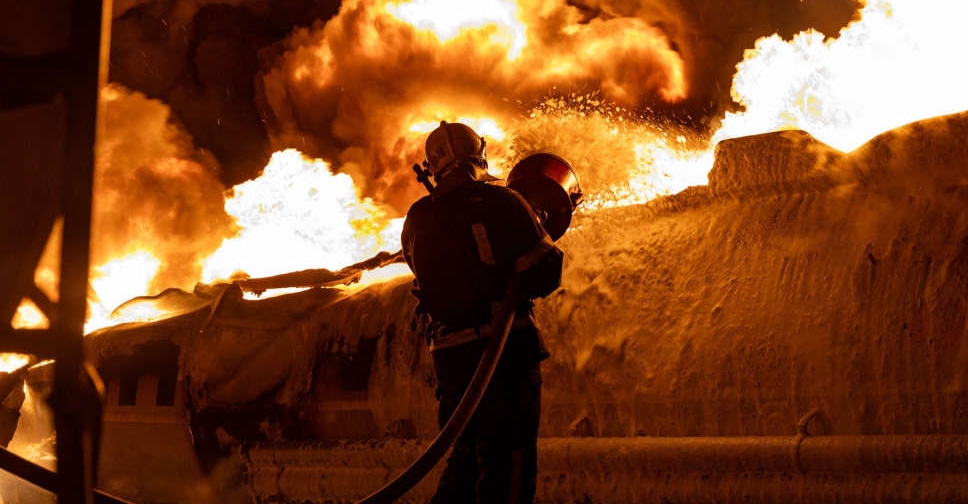 One dead as Ukraine's two largest cities under Russian attack
One dead as Ukraine's two largest cities under Russian attack



